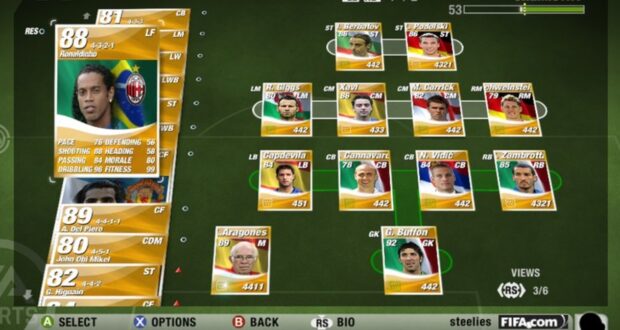
The fusion of technology and entertainment in the world of video gaming has birthed captivating virtual economies, none more compelling than the realm of FIFA Ultimate Team (FUT).
This groundbreaking game mode, nestled within the globally acclaimed EA Sports FIFA series, has not only redefined the way enthusiasts experience football simulation but has also established an intricate digital marketplace through its player trading, in-game currencies, and innovative mechanics.
The emergence of FUT as a virtual economy showcases how gaming can transcend traditional boundaries to become a dynamic economic ecosystem of its own.
The Genesis of FIFA Ultimate Team (FUT)
FUT’s origins trace back to the integration of offline content in the UEFA Champions League 2006/07 and its subsequent inclusion in FIFA 09 as DLC.
The initial concept was relatively straightforward: allow players to build a custom football team by collecting player cards through packs, earned or purchased with in-game currency.
These players could then be assembled into squads and used to compete against both AI-controlled and online opponents. However, what began as a simple addition quickly blossomed into a phenomenon that would shape the future of in-game economies.
The Birth of a Virtual Economy
At the heart of FUT’s transformation into a virtual economy lies its in-game currency, FIFA Coins. These coins can be earned through various in-game activities such as playing matches, completing challenges, and selling unwanted player cards.
This in-game currency is the cornerstone of FUT’s economy, as players use it to purchase packs containing player cards, contracts, consumables, and other items that enhance their teams’ performance.
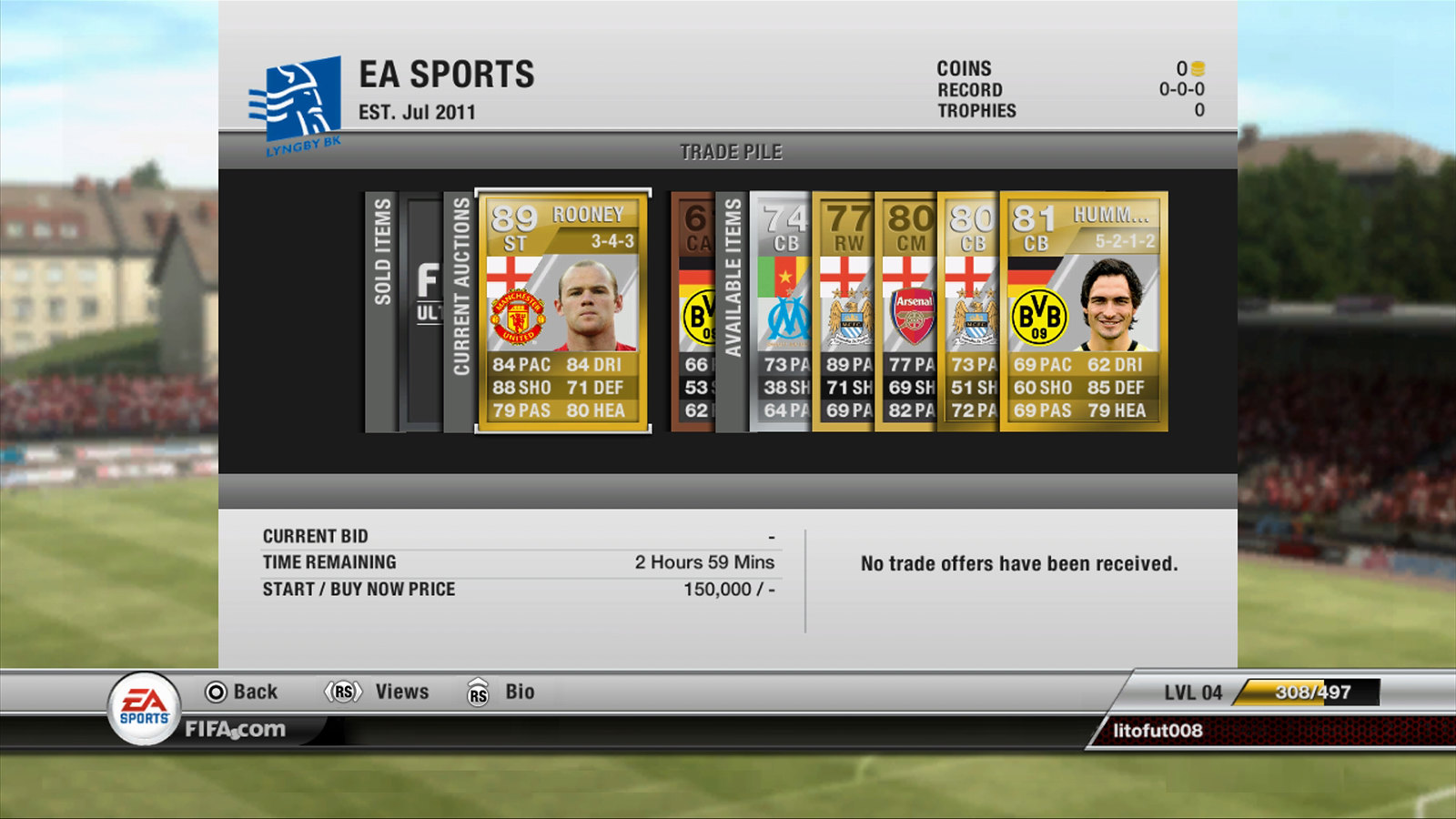
However, the key innovation that turned FUT into a virtual economy was the introduction of player trading. Each player card possesses a value dictated by various factors including player rating, rarity, popularity, and current in-game performance.
Players can buy, sell, and trade these cards on the in-game transfer market, where supply and demand dynamics shape their prices. This trading system laid the foundation for a burgeoning economy, where astute traders could amass wealth by exploiting market trends, buying low and selling high.
The Rise of FUT as a Digital Marketplace
As the popularity of FUT surged, players’ interests shifted from merely competing on the pitch to engaging in the transfer market. What started as a side activity soon became an intricate web of strategies, speculation, and transactions.
Players who honed their trading skills found themselves accumulating virtual wealth, enabling them to assemble dream squads that could rival even the most elite football clubs.
This digital marketplace within FUT gave rise to an entire ecosystem. Market analysis websites and social media accounts emerged, offering insights, tips, and predictions about player values.
Online forums and communities buzzed with discussions about trading techniques and investment opportunities. YouTube and Twitch became platforms for content creators to share their trading experiences and strategies, amassing dedicated followings in the process.
Challenges and Controversies
As FUT’s virtual economy thrived, it also encountered its fair share of challenges and controversies. The introduction of microtransactions allowed players to purchase FIFA Points, which could be exchanged for packs containing player cards.
This feature fueled debates about the ethics of loot boxes and the potential for fostering addictive behaviors among players, particularly younger ones. Some argued that the system resembled the best online betting sites in South Africa, as players spent real money for a chance to get valuable player cards.
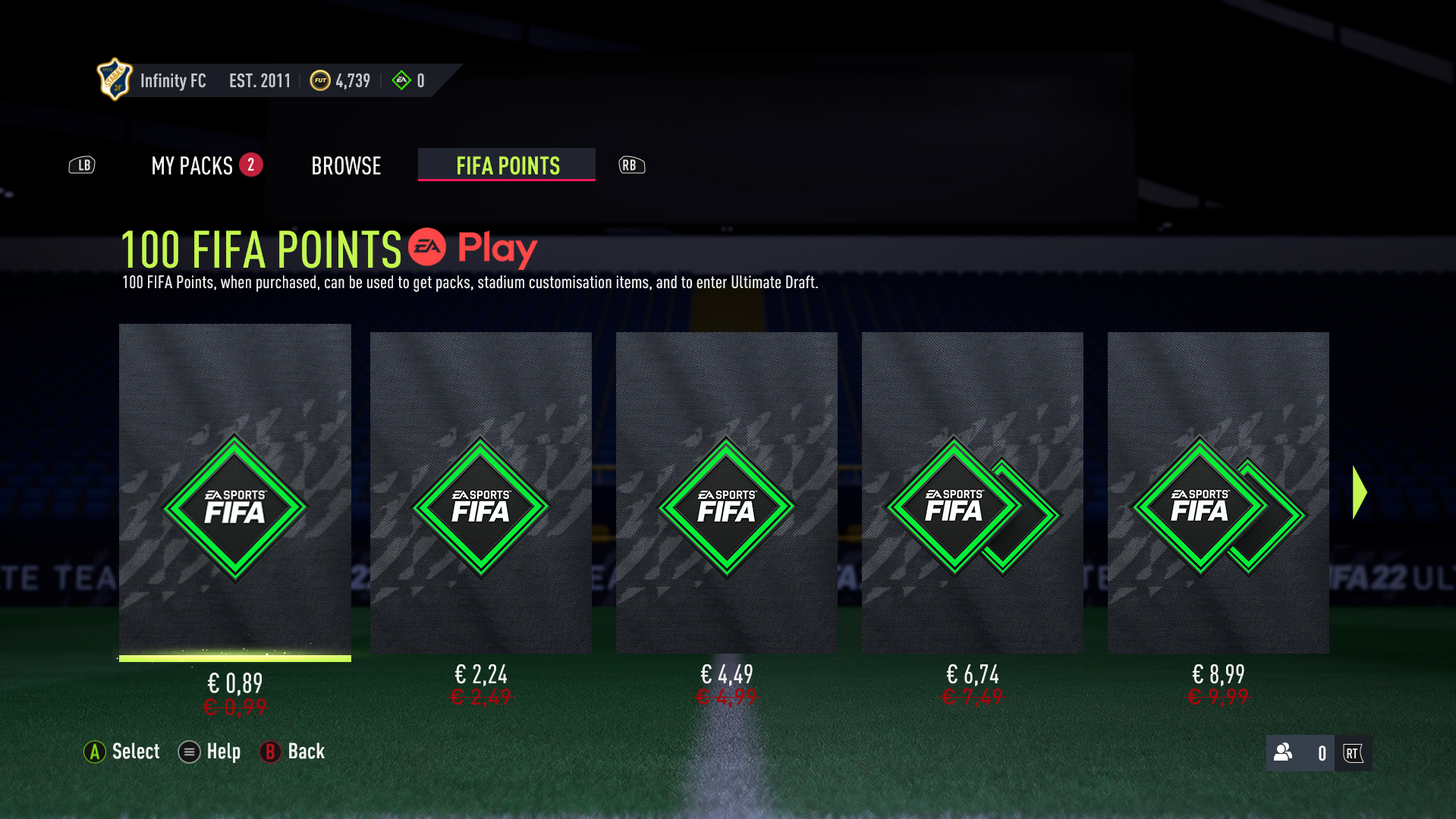
Additionally, a subset of players turned to external websites to purchase FIFA Coins using real-world currency, bypassing the need to engage in in-game trading or purchase FIFA Points.
This practice, known as coin buying, not only compromised the integrity of the in-game economy but also led to concerns about security breaches and unauthorized transactions.
Evolution and Future Prospects
Over the years, FUT has evolved with new features, modes, and improvements, all of which have continued to influence its virtual economy.
The introduction of Squad Building Challenges (SBCs) added a layer of complexity by allowing players to earn rewards through completing specific squad-building tasks. This further altered market dynamics, as players speculated on potential SBC requirements and invested accordingly.

Looking ahead, the future of FUT’s virtual economy is likely to be shaped by ongoing advancements in technology, gaming culture, and regulatory considerations.
As the discussion around loot boxes and microtransactions intensifies, game developers may need to adapt their monetization strategies to maintain player engagement while addressing concerns about fairness and addiction.
Final Thoughts
FIFA Ultimate Team stands as a testament to the incredible potential of virtual economies within the gaming world. What started as a mode for building custom football squads has transformed into a vibrant digital marketplace, complete with trading, speculation, and intricate strategies.
FUT’s virtual economy has captivated players and generated discussions about gaming ethics, player behavior, and the convergence of sports and technology.
As the gaming industry continues to evolve, the legacy of FIFA Ultimate Team’s virtual economy will undoubtedly leave a lasting impact on both the gaming landscape and the broader conversations about the intersection of entertainment and economics.
 FIFA Infinity The Absolute FIFA Site
FIFA Infinity The Absolute FIFA Site